
Geographical analysis
Department of Geography & GIS

Department of Geography & GIS
Geographical analysis
Year: 2024, Volume: 13, Issue: 2, Pages: 20-26
Original Article
K Chandramohan1∗, P Elayapillai1,2, M A Sivaraman1
1Tribal Research Centre, Tamil University, Thanjavur, Tamil Nadu, India
2Department of Literature, Tamil University, Thanjavur, Tamil Nadu, India
*Corresponding Author
Email: [email protected]
Received Date:24 July 2024, Accepted Date:12 September 2024
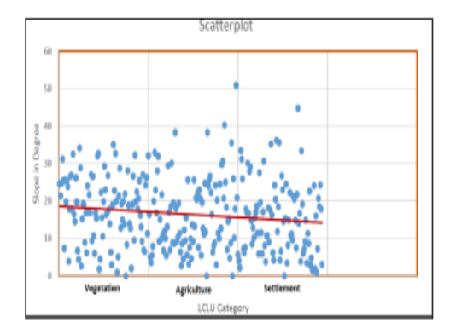
Accessing localized information in densely forested areas poses significant challenges. This study utilizes Sentinel-2 imagery with 10m NDVI data to derive a detailed vegetation map, complemented by high-resolution Google Earth feature identification for cross-verification. The primary aim is to map the forest landscape comprehensively and analyze the spatial patterns of settlements and forest-agriculture interactions within the forest, using publicly available data sources. The study specifically examines areas with slopes exceeding 23.8 degrees, which are unsuitable for settlements due to the heightened risk of landslides. By correlating NDVI data with slope calculations through a multiple linear regression model, the study identifies significant statistical relationships, with an R² value of 0.2 and a P-value of 0.006. Results indicate that the forest's spatial structure supports two distinct settlement patterns: linear settlements on slopes ranging from 0 to 8.6 degrees and scattered settlements on slopes between 16.22 and 23.79 degrees. These findings highlight the critical influence of slope on settlement distribution. This research provides valuable insights into the living environments of forest residents and underscores the importance of sustainable forest ecosystem management.
Keywords: Remote Sensing, Recoding, Unsupervised classification, NDVI, LCLU, DEM, Sirumalai, Settlement pattern 2
© 2024 Chandramohan et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Published By Bangalore University, Bengaluru, Karnataka
Subscribe now for latest articles and news.