
Geographical analysis
Department of Geography & GIS

Department of Geography & GIS
Geographical analysis
DOI: 10.53989/bu.ga.v11i2.22.4
Year: 2022, Volume: 11, Issue: 2, Pages: 16-29
Original Article
Bharat Gadakh1*, Ravindra Jaybhaye2
1Department of Geography, KTHM College, Nashik
2Professor, Department of Geography, SPPU, Pune
*Corresponding Author
Email: [email protected]
Received Date:02 April 2022, Accepted Date:22 December 2022
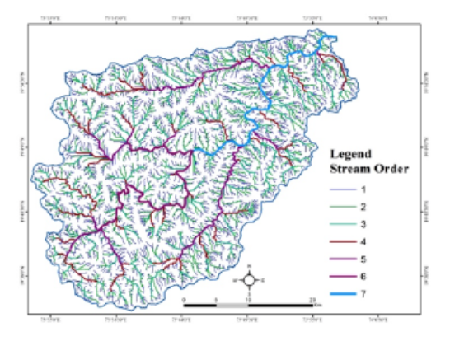
The rapid growth of urbanization, industrialization, an exponential increase in population and change of climate along with uneven distribution of rainfall make proper water management and planning of storage is very challenging. Satellite-based geoinformatics technology has supported to be an efficient tool in the analysis of drainage networks, surface morphological features, and interrelation with groundwater management at the watershed level. Geoinformatics approach such as remote sensing and Geographic information system has used for extraction of watershed analysis using Cartosat Digital Elevation Model (DEM) satellite images for assessment of drainage and extraction of their relative parameters For the Darna watershed in Nashik district, Maharashtra. In the study Hydrological parameters drainage analysis, topographical parameters, and land-use patterns has evaluated and interpreted for sustainable watershed management. The results reveals that Cartosat Data Dem based hydrological evaluation of watershed-scale is applied and accurate compared to available various technique.
Keywords: CARTOSAT-DEM, Geoinformatics, LISSIV, Darna Basin, Watershed
© 2022 Gadakh & Jaybhaye. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Published By Bangalore University, Bengaluru, Karnataka
Subscribe now for latest articles and news.