
Geographical analysis
Department of Geography & GIS

Department of Geography & GIS
Geographical analysis
Year: 2019, Volume: 8, Issue: 2, Pages: 76-82
Original Article
K N Ashwatha1, A S Rayamane2
1Research Scholar, Department of Geography & Geoinformatics, Bangalore University, 560056,
Bengaluru
2Department of Geography & Geoinformatics, Bangalore University, 560056, Bengaluru
Received Date:08 July 2019, Accepted Date:11 November 2019
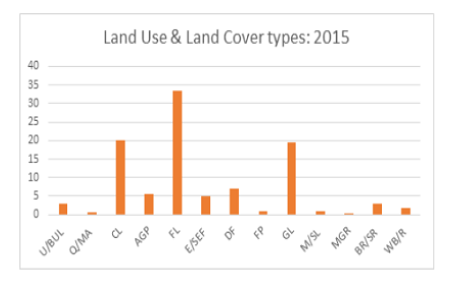
This study examines the accuracy assessment of land use and land cover classification using Google Earth in identifying grassland boundaries in Karnataka for the year 2015. For this study, LANDSAT_8 The Operational Land Imager (OLI)Thermal Infrared Sensor (TIRS) images of the 2015 were used and analysed using ArcGIS 10.1. Supervised classification scheme was used to classify the images. Under land use and land cover categories Urban/Built-up land, Quarry/Mining Area, Crop land, Agricultural plantation, Fallow land, Evergreen/Semievergreen forest, Deciduous Forest, Forest plantation, Grasslands, Marshy/swampy land, Mangrove, Barren Rocky/Sheet Rock and Water Bodies/Rivers were studied. After classification of land use and land cover types, 277 points from random sampling for the year 2015 were generated in Arc GIS and converting random points to KML in order to open in Google Earth. Each random points value verified from Google Earth for accuracy assessment. Google Earth model was used to measure of how many ground truth pixels are correctly classified. For this study, Free Google Earth which was Built in Satellite images of the study periods were used. The result shows that overall accuracy or total accuracy obtained is 82. 67% with kappa statistics of 0.8102 (81.02%) in 2015 which is acceptable in both accuracy total (overall) and Kappa accuracy.
Keywords: Grasslands; Land Use Land Cover; Google Earth; Accuracy Assessment; Kappa
© 2019 Ashwatha & Rayamane. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium provided the original author and source are credited.
Published By Bangalore University, Bengaluru, Karnataka
Subscribe now for latest articles and news.