
Geographical analysis
Department of Geography & GIS

Department of Geography & GIS
Geographical analysis
Year: 2021, Volume: 10, Issue: 2, Pages: 12-18
Original Article
V Parameswari1*, V Emayavaramban2
1Research Scholar, Department of Geography, Madurai Kamaraj University, Madurai, 625 021
2Professorand Head, Department of Geography, Madurai Kamaraj University, Madurai, 625 021
*Corresponding Author
Email: [email protected]
Received Date:16 January 2021, Accepted Date:21 May 2021
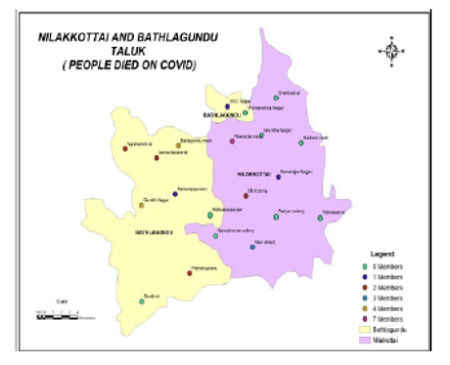
The most recently discovered corona virus causes corona virus disease COVID-19. COVID -19 is the infectious disease caused by the most recently discovered corona virus. This new virus and disease were unknown before the outbreak began in Wuhan, China, in December 2019. A qualitative approach was adopted for the study. The study utilized the krejcie and Morgan sample size table for determining the sample size (Krejcie & Morgan, 1970, For the present study the secondary data has been obtained from the 2020-2022, government reports and Nilakottai and Batlagundu government hospital and unpublished records. In Nilakotti taluk is business area in famous for gold smith and flower marketing so mostly other district peoples were come from in the market sources to Nilakottai taluk. So the people came from higher density to Nilakottai taluk. This is factor of corono virus spread in Nilakottai Block. Batlagundu in main junction of tourist visits because of kodaikanal near to this block and it connects with the main district of Dindigul, Theni and Madurai network also connected in the central of Batlagundu So the people moving from Academic, Business, Tourist, Medical, Administrative all the orientation in Batlagundu. So it is easily affected in the covid 19. In Nilakottai taluk the lockdown is successful by the help of health inspector and taluk officer are much more effect to control population movements, and infection areas were closed, and maintain the spread& split out the prevention powder and the medicine, herbal water vitamin C tablet and nila vembu kasayam and distributed by the people in in the street, these all factors were control by the covid 19 were not spread out in the Nilakottai taluk.
Keywords: Corona -Affected; Recover; Death Ratio; R0 Factor
© 2021 Parameswari & Emayavaramban. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Published By Bangalore University, Bengaluru, Karnataka
Subscribe now for latest articles and news.